Understanding Proton Transfer in Acid-Base Reactions
In acid-base chemistry, each acid forms a conjugate base after donating a proton, and each base forms a conjugate acid after accepting a proton. These are always found in pairs, known as conjugate acid-base pairs.
What is a Conjugate Acid?
A conjugate acid is the species formed when a base accepts a proton (H+).
What is a Conjugate Base?
A conjugate base is the species formed when an acid donates a proton (H+).
Explanation with Example:
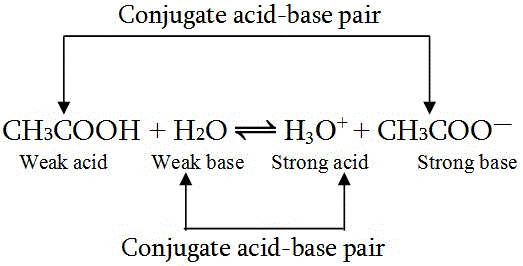
Proton transfer occurs in both forward and reverse reactions. For example:
In the forward reaction, CH3COOH donates a proton to H2O, making CH3COOH a Bronsted-Lowry acid and H2O a base. In the reverse reaction, CH3COO- accepts a proton from H3O+, acting as a base while H3O+ is the conjugate acid.
What is a Conjugate Acid-Base Pair?
A conjugate acid-base pair consists of two substances that differ only by a single proton (H+). They exist on opposite sides of a reversible reaction:
- CH3COOH / CH3COO- → Acid / Conjugate base
- H2O / H3O+ → Base / Conjugate acid
Key Points to Remember:
- A weak acid has a strong conjugate base.
- A weak base has a strong conjugate acid.
- A strong acid has a weak conjugate base.
- A strong base has a weak conjugate acid.
🔗 Other Useful Links
- News By Amurchem
- Free Web Development Course
- All-in-One Exam Prep Portal
- Articles by Amurchem
- Grade 12 Section
- Grade 11 Section
- Grade 10 Section
- Grade 09 Section
- Home and Online Tuition
- Labs By Amurchem
- Science Lectures By Amurchem
© 2025 AmurChem. All rights reserved.