Abstract
This experiment aimed to investigate the effect of tonicity on plasmolysis and deplasmolysis in plant cells. By subjecting onion epidermal cells to solutions of varying tonicity, changes in cell morphology were observed. The results provide insights into the behavior of plant cells under different osmotic conditions.
Introduction
Plasmolysis is the process in which plant cells lose water in a hypertonic solution, causing the protoplast to shrink away from the cell wall. Deplasmolysis, on the other hand, occurs when the cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, causing it to regain water and return to its original turgid state. This experiment aims to understand the relationship between tonicity and plasmolysis, as well as deplasmolysis, in plant cells.
Experimental Details
Materials
- Onion bulbs
- Microscope
- Microscope slides
- Coverslips
- Distilled water
- Salt solutions of varying concentrations
- Blotting paper
Procedure
- Prepare a salt solution of known concentration (e.g., 0.5M).
- Peel off a thin layer of the epidermis from an onion bulb.
- Place the onion epidermal strip on a microscope slide.
- Add a drop of the prepared salt solution to the epidermal strip.
- Cover the slide with a coverslip, ensuring no air bubbles are trapped.
- Observe the cells under the microscope at low magnification.
- Record any changes in cell morphology, such as plasmolysis.
- Repeat steps 3-7 using salt solutions of different concentrations.
Observations and Calculations
Record the following observations for each salt solution concentration:
| Salt Solution Concentration (M) | Cell Morphology |
|---|---|
| 0 (Distilled water) | Turgid cells |
| 0.1 | Slight shrinkage |
| 0.5 | Partial plasmolysis |
| 1.0 | Complete plasmolysis |
Calculate the percentage of plasmolysis using the formula:
\[ \% \text{Plasmolysis} = \left( \frac{\text{Initial cell size} - \text{Plasmolyzed cell size}}{\text{Initial cell size}} \right) \times 100 \]
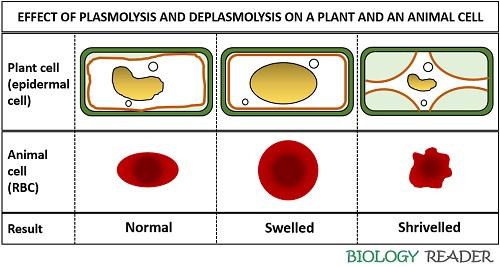 |
| Effect of tonicity on plasmolysis and deplasmolysis |
Conclusion
The experiment demonstrates that the tonicity of the solution directly affects the plasmolysis and deplasmolysis of plant cells. Cells exposed to hypertonic solutions undergo plasmolysis, while those in hypotonic solutions experience deplasmolysis. These findings contribute to our understanding of cell physiology and osmotic regulation in plants.
Precautions
- Handle microscope slides and coverslips carefully to avoid breakage.
- Use sharp blades to obtain thin onion epidermal strips.
- Ensure that the microscope is properly focused to obtain clear observations.
- Dispose of salt solutions properly to prevent environmental contamination.
Short Questions for Determination of Tonicity Effect
-
What is plasmolysis?
Plasmolysis is the process in plant cells where the cell membrane shrinks away from the cell wall due to the loss of water when placed in a hypertonic solution.
-
Explain the concept of tonicity.
Tonicity refers to the relative concentration of solutes in two solutions separated by a semipermeable membrane. It determines the direction and extent of osmosis.
-
How does plasmolysis occur?
Plasmolysis occurs when a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, causing water to move out of the cell, resulting in the shrinking of the protoplast away from the cell wall.
-
What is deplasmolysis?
Deplasmolysis is the reversal of plasmolysis, where a plant cell regains water and returns to its original turgid state when placed in a hypotonic solution.
-
How can you observe plasmolysis?
Plasmolysis can be observed under a microscope by placing plant cells in a hypertonic solution and observing the shrinking of the cytoplasm away from the cell wall.
-
What is the importance of the experiment?
The experiment helps in understanding how cells respond to changes in their external environment, particularly in terms of osmotic pressure and tonicity.
-
Describe the procedure for conducting the experiment.
The procedure involves preparing plant cells on microscope slides, placing them in solutions of varying tonicity, and observing changes under a microscope.
-
What are the different types of solutions used in the experiment?
The solutions used include hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic solutions.
-
How does tonicity affect plasmolysis?
Tonicity determines the direction of water movement. In hypertonic solutions, water moves out of the cell, leading to plasmolysis, while in hypotonic solutions, water moves into the cell, causing it to swell.
-
What are the key observations to make during the experiment?
Key observations include changes in cell shape, movement of cytoplasm, and alterations in cell volume.
-
Explain the role of osmosis in plasmolysis.
Osmosis is the process by which water moves across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. In plasmolysis, osmosis leads to the loss of water from the cell.
-
How does plasmolysis affect cell turgidity?
Plasmolysis causes a loss of turgor pressure, leading to a decrease in cell turgidity.
-
What are the factors influencing the degree of plasmolysis?
The concentration gradient between the cell and the surrounding solution, as well as the permeability of the cell membrane, influence the degree of plasmolysis.
-
How does plasmolysis relate to plant wilting?
Plasmolysis is related to plant wilting as it involves the loss of water from plant cells, leading to a decrease in cell turgidity and overall wilted appearance of the plant.
-
Compare and contrast plasmolysis and deplasmolysis.
Plasmolysis involves the shrinking of the protoplast away from the cell wall in a hypertonic solution, while deplasmolysis involves the reversal of this process when the cell is placed in a hypotonic solution.
-
What are the potential applications of understanding plasmolysis?
Understanding plasmolysis is important in agriculture, as it helps in understanding plant responses to drought conditions and in developing strategies for crop management.
-
Discuss the significance of the experiment in cell biology.
The experiment provides insights into the fundamental processes of osmosis, cell membrane permeability, and cell turgor pressure, which are crucial in understanding cell physiology and biology.
-
How can the results of the experiment be applied in real-life situations?
The results can be applied in various fields such as agriculture, medicine, and biotechnology to understand and manipulate cellular responses to different environmental conditions.
-
What are the limitations of the experiment?
Limitations include variations in cell size and shape, as well as the potential for experimental errors in preparation and observation.
-
How can the experiment be improved?
The experiment can be improved by standardizing procedures, using more precise measurement techniques, and exploring additional variables.
-
What are the safety precautions to be taken during the experiment?
Safety precautions include handling chemicals and biological materials properly, wearing protective gear, and following established laboratory protocols.
MCQs for Determination of Tonicity Effect
-
What is the purpose of determining the effect of tonicity on plasmolysis and deplasmolysis?
- To observe the movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane.
- To study the effects of different solute concentrations on cell membrane integrity.
- To investigate the process of cellular respiration in plant cells.
- To determine the optimal pH for enzyme activity in Red Blood Cells.
Answer: b. To study the effects of different solute concentrations on cell membrane integrity.
-
Which type of cells are commonly used in the experiment to study plasmolysis?
- Animal cells.
- Plant cells.
- Bacterial cells.
- Fungal cells.
Answer: b. Plant cells.
-
What happens to a plant cell placed in a hypertonic solution?
- It gains water, causing turgor pressure to increase.
- It loses water, causing the cell membrane to shrink away from the cell wall.
- There is no change in the cell's water content.
- It undergoes photosynthesis at an increased rate.
Answer: b. It loses water, causing the cell membrane to shrink away from the cell wall.
-
What is the term for the process of returning a plasmolyzed cell to its original state?
- Plasmolysis.
- Deplasmolysis.
- Osmosis.
- Hypotonicity.
Answer: b. Deplasmolysis.
-
In the experiment involving Red Blood Cells, what solution is typically used to induce hemolysis?
- Hypertonic saline solution.
- Hypotonic saline solution.
- Isotonic saline solution.
- Distilled water.
Answer: d. Distilled water.
🔗 Other Useful Links
- News By Amurchem
- Free Web Development Course
- All-in-One Exam Prep Portal
- Articles by Amurchem
- Grade 12 Section
- Grade 11 Section
- Grade 10 Section
- Grade 09 Section
- Advanced Artificial Course
- Home and Online Tuition
- Labs By Amurchem
- Science Lectures By Amurchem
- Social Media Executive Course
© 2025 AmurChem. All rights reserved.






