Abstract:
This experiment aims to examine different types of plant storage organs, including bulbs (onion), corms (Edocasia), rhizomes (ginger), and stem tubers (potato), and explore their cultivation methods to obtain new plants.
Introduction:
In this experiment, we examine various plant storage organs to understand their structures and mechanisms of propagation. Bulbs, corms, rhizomes, and stem tubers are essential for vegetative propagation in many plant species. By studying their characteristics and cultivation techniques, we can gain insights into efficient plant propagation methods.
Bulbs, such as onions, consist of concentric layers of modified leaves surrounding a central bud. Corms, like Edocasia, are solid storage organs with a swollen stem base. Rhizomes, exemplified by ginger, are underground stems that grow horizontally. Stem tubers, such as potatoes, are enlarged underground stems for storing nutrients.
Procedure:
- Collect specimens of onion bulb, Edocasia corm, ginger rhizome, and potato stem tuber.
- Examine each specimen under a microscope to observe their internal structures.
- Prepare suitable growing conditions for each plant type.
- Plant the specimens in appropriate soil and water regularly.
- Monitor growth and development over a specified period.
- Document any visible changes and record observations.
Observations:
Table 1: Observations of Plant Storage Organs
| Plant Type | Characteristics | Observations |
|---|---|---|
| Onion Bulb | Concentric layers, central bud | Increased root growth, sprouting of new shoots |
| Edocasia Corm | Swollen stem base | Emergence of new cormels |
| Ginger Rhizome | Horizontal underground stem | Development of new shoots along the rhizome |
| Potato Stem Tuber | Enlarged underground stem | Formation of new eyes and sprouts |
 |
| Onion Bulb |
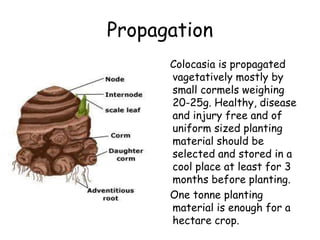 |
| Edocasia Corm |
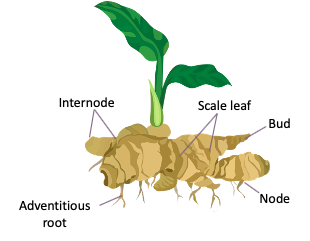 |
| Ginger Rhizome |
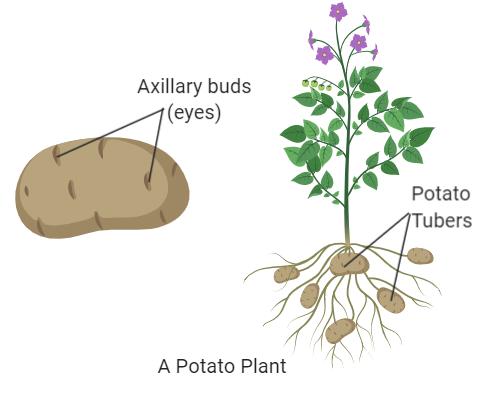 |
| Potato Stem Tuber |
Calculations:
No calculations required for this experiment.
Precautions:
- Handle plant specimens carefully to avoid damage.
- Ensure proper environmental conditions for optimal growth.
- Regularly monitor the specimens for any signs of disease or pest infestation.
- Use sterilized equipment to prevent contamination.
- Follow safety guidelines when handling soil and gardening tools.
Experiment Questions and Answers
-
What is the purpose of this experiment?
The purpose of this experiment is to examine different types of plant storage organs and explore their cultivation methods to obtain new plants.
-
What are the four types of plant storage organs examined in this experiment?
The four types of plant storage organs examined are bulbs (onion), corms (Edocasia), rhizomes (ginger), and stem tubers (potato).
-
Describe the structure of an onion bulb.
An onion bulb consists of concentric layers of modified leaves surrounding a central bud.
-
What is the characteristic feature of an Edocasia corm?
The characteristic feature of an Edocasia corm is its swollen stem base.
-
Explain the function of a ginger rhizome.
A ginger rhizome is an underground stem that grows horizontally and serves as a storage organ for nutrients. It also produces new shoots.
-
How does a potato stem tuber propagate?
A potato stem tuber propagates by forming new eyes or sprouts that develop into new plants.
-
What are the steps involved in the procedure of this experiment?
The steps involved in the procedure include specimen collection, microscopic examination, preparation of growing conditions, planting, monitoring, and documentation.
-
What observations are recorded for each plant type?
Observations include changes in root growth, sprouting of new shoots, emergence of cormels (in the case of Edocasia corm), development of new shoots along the rhizome (in ginger), and formation of new eyes and sprouts (in potatoes).
-
Why is it important to handle plant specimens carefully?
It is important to handle plant specimens carefully to avoid damage that could affect their growth and development.
-
What precautions should be taken during the experiment?
Precautions include handling specimens carefully, ensuring proper environmental conditions, monitoring for signs of disease or pest infestation, using sterilized equipment, and following safety guidelines.
-
What are the benefits of studying plant storage organs?
Studying plant storage organs provides insights into vegetative propagation methods, which are important for agricultural and horticultural practices, as well as for understanding plant biology.
-
How do you distinguish between a bulb and a corm?
A bulb consists of concentric layers of modified leaves surrounding a central bud, while a corm is a solid storage organ with a swollen stem base.
-
What environmental conditions are required for optimal plant growth?
Optimal plant growth requires suitable soil, adequate water, proper temperature, and sufficient light.
-
How do you prevent contamination during the experiment?
Contamination can be prevented by using sterilized equipment and following hygiene practices.
-
What is the role of nutrients in plant growth?
Nutrients are essential for plant growth as they provide the necessary elements for metabolic processes and structural development.
-
How do you document observations during the experiment?
Observations can be documented using written notes, photographs, or digital recordings.
-
What factors might affect the growth of plant specimens?
Factors such as temperature fluctuations, inadequate light, water stress, nutrient deficiencies, and pest infestation can affect the growth of plant specimens.
-
What are the advantages of vegetative propagation?
Vegetative propagation allows for the rapid multiplication of desirable plant traits, maintains genetic uniformity, and enables the production of plants that are true to type.
-
How can you identify signs of disease in plant specimens?
Signs of disease in plant specimens include wilting, yellowing of leaves, lesions, abnormal growths, and presence of pests or pathogens.
-
What are some common pests and diseases that affect plant growth?
Common pests and diseases include aphids, fungi (such as powdery mildew and rust), bacterial infections, and viral diseases.
Experiment Multiple Choice Questions
-
What is the main objective of examining plant storage organs in this experiment?
Answer: B. To explore methods of vegetative propagation
-
Which of the following plant storage organs is characterized by concentric layers of modified leaves?
Answer: D. Bulb
-
What is the characteristic feature of a ginger rhizome?
Answer: C. Horizontal underground stem
-
How do potato stem tubers propagate?
Answer: D. By forming new eyes or sprouts
-
What precautions should be taken during the experiment to prevent contamination?
Answer: D. All of the above
🔗 Other Useful Links
- News By Amurchem
- Free Web Development Course
- All-in-One Exam Prep Portal
- Articles by Amurchem
- Grade 12 Section
- Grade 11 Section
- Grade 10 Section
- Grade 09 Section
- Advanced Artificial Course
- Home and Online Tuition
- Labs By Amurchem
- Science Lectures By Amurchem
- Social Media Executive Course
© 2025 AmurChem. All rights reserved.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/corms-different-from-bulbs-tubers-and-rhizomes-2131032_v2-cdd3221512504b33908cf8d32549e2b3.png)