Abstract
In this experiment, animal cells from frog's blood and plant cells from onion epidermis were examined under a microscope using temporary staining techniques like iodine or methylene blue. The aim was to observe and compare the differences in the structures of animal and plant cells.
Introduction
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of living organisms. Animal and plant cells exhibit distinct characteristics due to differences in their structures and functions. The purpose of this experiment is to observe and compare the structural differences between animal and plant cells. Frog's blood and onion epidermis were chosen as representative specimens of animal and plant cells, respectively. Temporary staining techniques such as iodine or methylene blue were employed to enhance the visibility of cellular structures under the microscope.
Experiment Details
Procedure
- Prepare slides of frog's blood and onion epidermis samples.
- Apply a drop of iodine or methylene blue stain on each slide.
- Place a coverslip over the stained sample gently to avoid air bubbles.
- Examine the slides under a compound microscope using low and high power objectives.
- Observe and compare the cellular structures of the animal and plant cells.
Observations
Observations:
- Animal Cell (Frog's Blood): [Describe observations]
- Plant Cell (Onion Epidermis): [Describe observations]
 |
| Frog's Blood Cells |
 |
| Onion Epidermis |
Conclusion
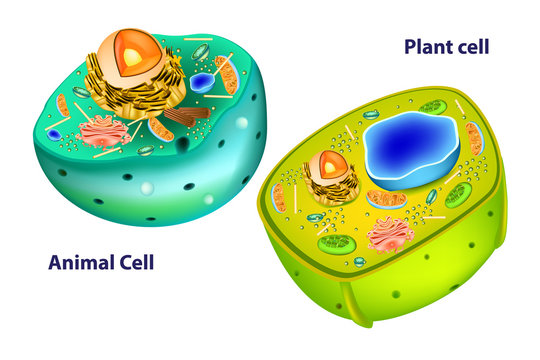
The experiment revealed distinct differences between animal and plant cells. Animal cells lacked a cell wall and had a round shape, while plant cells had a rigid cell wall and a rectangular shape. Additionally, plant cells contained chloroplasts, which were absent in animal cells. The staining techniques aided in visualizing cellular structures more clearly under the microscope.
Precautions
- Handle microscope slides and coverslips carefully to avoid breakage.
- Avoid over-staining the samples, as it may obscure cellular details.
- Clean the microscope lenses before and after use to ensure clarity of observation.
Short Questions with Answers
- What are the basic structural and functional units of living organisms?
- What is the function of a cell wall in plant cells?
- What is the function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
- What are the main components of a typical animal cell?
- What is the function of the nucleus in a cell?
- Which organelle is known as the "powerhouse" of the cell?
- What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
- What is the difference between rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
- What are vacuoles and what is their function in plant cells?
- What is the role of Golgi apparatus in the cell?
- What is the function of ribosomes in the cell?
- What distinguishes eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells?
- What is the role of the cytoskeleton in the cell?
- What is the function of lysosomes?
- What are the similarities and differences between plant and animal cells?
- What is the function of the cell membrane?
- What is the function of the nucleolus?
- What are the three components of the cell theory?
- What is the difference between plant and animal cell division?
- What is the significance of studying cell structure and function?
Answer: Cells.
Answer: The cell wall provides structural support and protection to the cell.
Answer: Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy.
Answer: Plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and organelles such as mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum.
Answer: The nucleus contains genetic material (DNA) and controls the cell's activities, including growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Answer: Mitochondria.
Answer: The endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein and lipid synthesis and transport within the cell.
Answer: Rough endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes attached to its surface and is involved in protein synthesis, while smooth endoplasmic reticulum lacks ribosomes and is involved in lipid metabolism and detoxification.
Answer: Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles filled with fluid. In plant cells, they store water, nutrients, and waste products, and help maintain turgor pressure.
Answer: The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other cellular locations.
Answer: Ribosomes are involved in protein synthesis by translating mRNA into polypeptide chains.
Answer: Eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles, while prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and organelles.
Answer: The cytoskeleton provides structural support, maintains cell shape, and facilitates cell movement and intracellular transport.
Answer: Lysosomes contain enzymes that break down waste materials and cellular debris through digestion.
Answer: Both plant and animal cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and organelles. However, plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and large central vacuoles, which are absent in animal cells.
Answer: The cell membrane regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell and maintains cell integrity and shape.
Answer: The nucleolus is involved in the production and assembly of ribosomal subunits.
Answer: The three components of the cell theory are: 1) all living organisms are composed of one or more cells, 2) the cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms, and 3) all cells come from pre-existing cells.
Answer: Plant cell division involves the formation of a cell plate during cytokinesis, while animal cell division forms a cleavage furrow.
Answer: Understanding cell structure and function is fundamental to understanding the biology of living organisms, including processes such as growth, development, and disease.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
- Which organelle is responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells?
- A. Golgi apparatus
- B. Chloroplast
- C. Mitochondria
- D. Endoplasmic reticulum
- What is the function of a cell wall in plant cells?
- A. Regulation of cell shape
- B. Protection and structural support
- C. Synthesis of proteins
- D. Storage of genetic material
- Which of the following is a characteristic feature of animal cells?
- A. Central vacuole
- B. Cell wall
- C. Chloroplast
- D. Nucleus
- Which staining technique is commonly used to visualize the nucleus of cells?
- A. Iodine
- B. Methylene blue
- C. Hematoxylin
- D. Eosin
- What is the function of the cytoplasm in cells?
- A. Synthesis of ATP
- B. Storage of genetic material
- C. Site of cellular respiration
- D. Site of metabolic activities
Answer: B. Chloroplast
Answer: B. Protection and structural support
Answer: D. Nucleus
Answer: C. Hematoxylin
Answer: D. Site of metabolic activities
🔗 Other Useful Links
- News By Amurchem
- Free Web Development Course
- All-in-One Exam Prep Portal
- Articles by Amurchem
- Grade 12 Section
- Grade 11 Section
- Grade 10 Section
- Grade 09 Section
- Advanced Artificial Course
- Home and Online Tuition
- Labs By Amurchem
- Science Lectures By Amurchem
- Social Media Executive Course
© 2025 AmurChem. All rights reserved.