Abstract
This experiment aims to analyze the external morphology of the mustard plant and perform microscopic examinations of its different anatomical parts including roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds. The study highlights significant structural adaptations that facilitate the survival, reproduction, and growth of the mustard plant.
Introduction
The mustard plant, belonging to the genus Brassica, is a significant crop due to its use in oil production and culinary applications. Understanding the structure of the plant from both a macroscopic and microscopic perspective can provide insights into its biological functions and evolutionary adaptations. The experiment covers external observations and detailed cellular examinations, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of plant morphology.
Experiment Details
Materials
- Mustard plants
- Light microscope
- Microscope slides and coverslips
- Staining reagents (Iodine, Methylene blue)
- Scalpel
- Camera for photomicrography
Procedure
- Observation of External Morphology: Examine the overall structure of the mustard plant including root system, stem, leaf patterns, flowers, and fruits.
- Sample Preparation: Carefully section the roots, stems, and leaves using a scalpel.
- Staining: Apply appropriate stains to enhance visibility of cellular structures under a microscope.
- Microscopic Examination: View prepared slides under various magnifications to observe cellular details in roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds.
- Data Recording: Take photographs and make sketches of significant findings.
Observations and Calculations
Details of observations for each part of the plant are meticulously recorded. The dimensions of observed cells and tissues are measured using the microscope's micrometer.
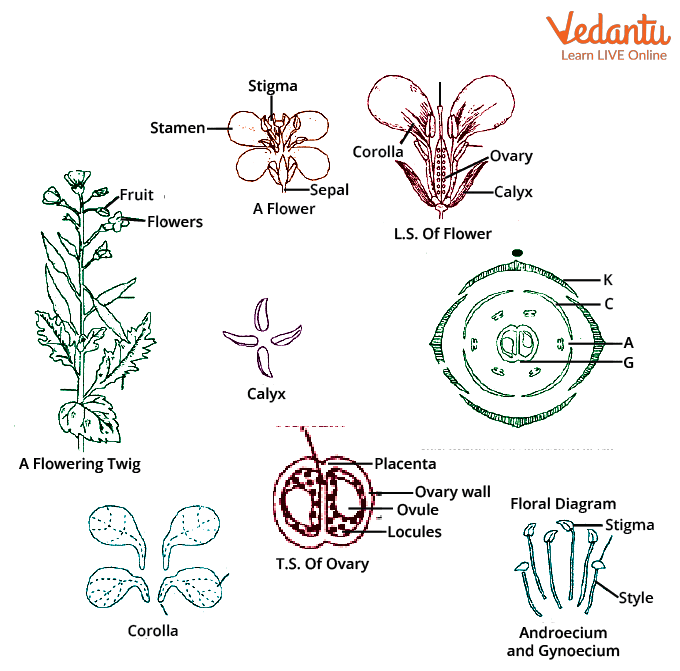 |
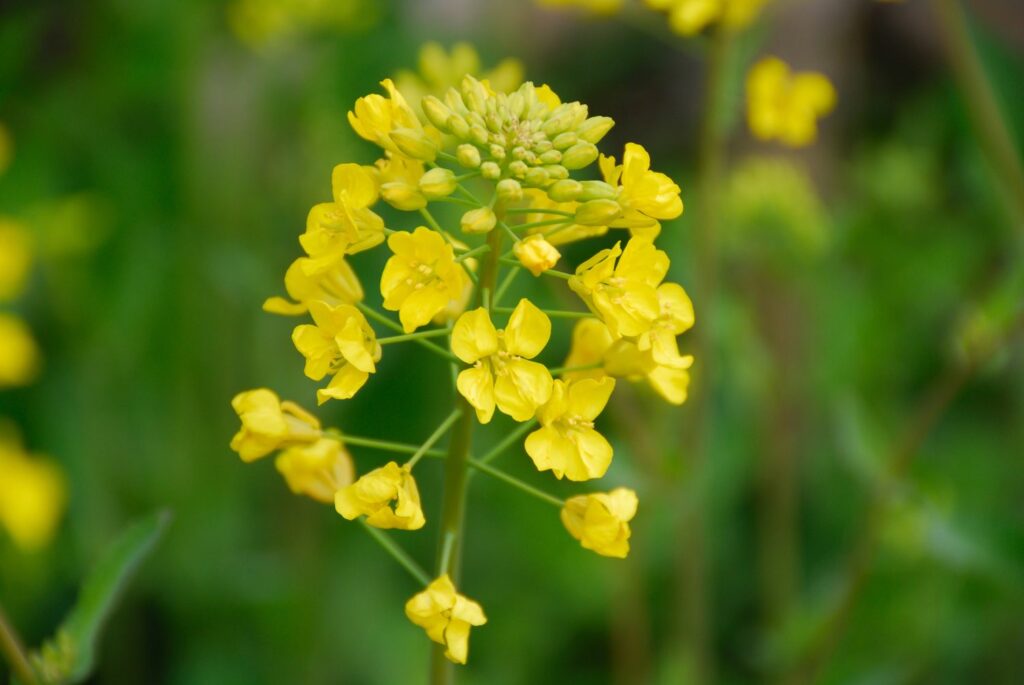
| External Morphology of Mustard Plant |
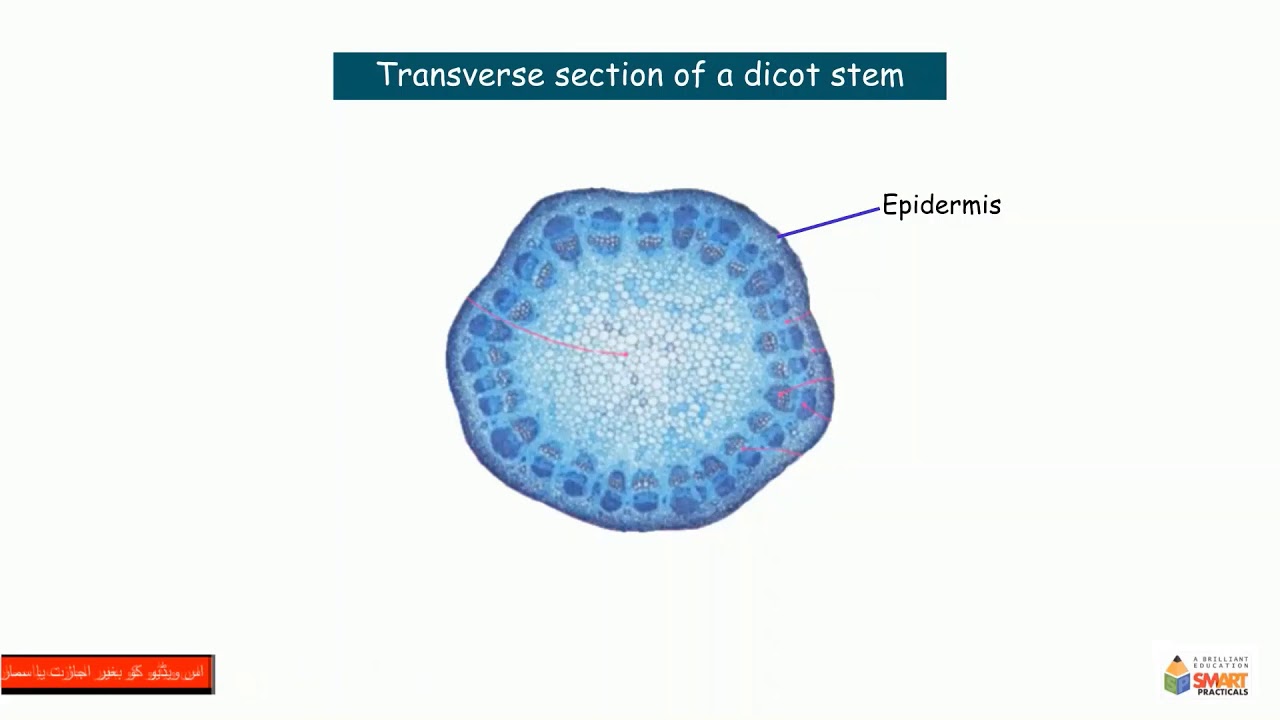 |
| Examination of Dicot Stem |
 |
| Examination of Leaf |
 |
| Mustard Plant Seed Under Microscope |
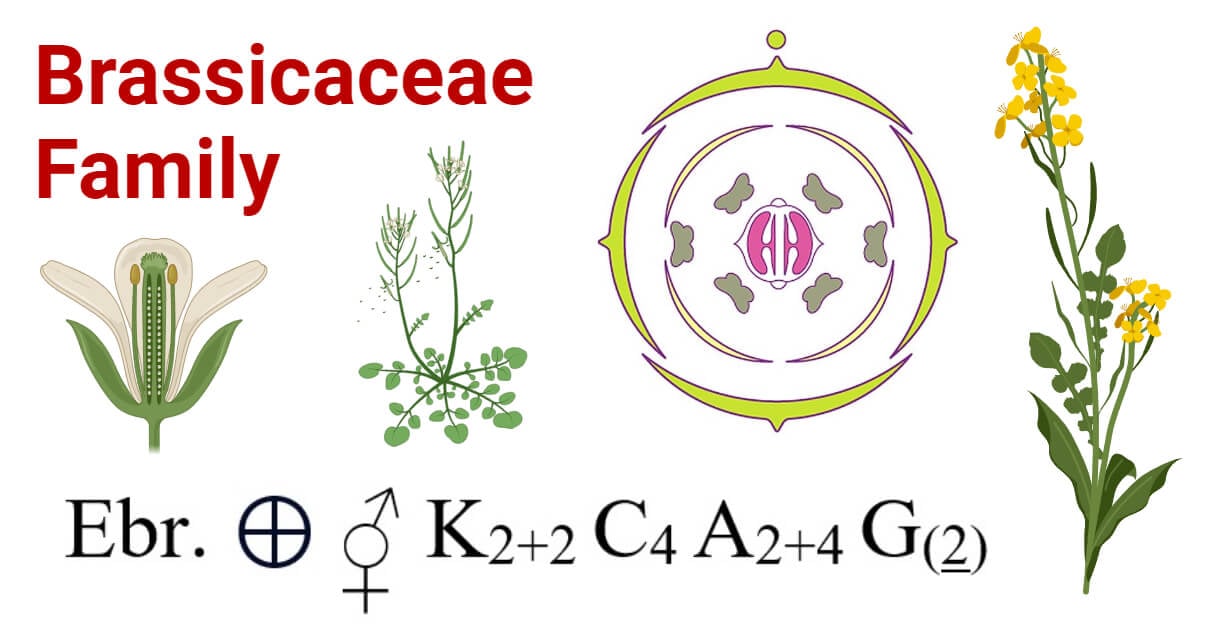 |
Brassicaceae Family |
Conclusion
The experiment concluded that the mustard plant exhibits several specialized structures in its roots, stems, and leaves that support its physiological processes. Microscopic examination revealed the presence of xylem, phloem, and other specialized cells that play roles in nutrition, support, and reproduction.
Precautions
- Handle the microscope and glass slides with care to avoid breakages.
- Use gloves and goggles when handling chemicals and stains.
- Ensure samples are thin enough to allow light to pass through for clear microscopy.
Examination Questions
Short Answer Questions
-
What is the scientific name of the mustard plant?
Answer: Brassica juncea. -
Describe the external morphology of a mustard plant.
Answer: Mustard plant is a herbaceous annual or biennial plant. It has a thick taproot system with a branched stem bearing alternate, simple leaves. Flowers are yellow and arranged in racemes. -
How do you prepare a microscopic slide of a mustard plant root?
Answer: To prepare a microscopic slide, slice a thin section of the root, stain with safranin, and mount it on a slide with a drop of water, cover it with a cover slip, and observe under a microscope. -
What are the characteristics of a mustard plant stem under the microscope?
Answer: Mustard plant stem shows vascular bundles arranged in a ring, with collenchyma and parenchyma tissues in the cortex and a pith in the center. -
Explain the microscopic structure of a mustard plant leaf.
Answer: A mustard plant leaf exhibits upper and lower epidermis, palisade and spongy mesophyll tissues, and stomata for gas exchange. -
What are the reproductive organs present in a mustard plant flower?
Answer: Mustard plant flower contains stamens (male reproductive organ) and pistil (female reproductive organ). -
Describe the process of pollination in mustard plant flowers.
Answer: Pollination in mustard plants occurs through both self-pollination and cross-pollination. Insects like bees and butterflies are the primary pollinators. -
What are the types of fruits produced by a mustard plant?
Answer: Mustard plant produces siliques, which are long, narrow fruits containing seeds. -
Discuss the structure of mustard plant seeds under the microscope.
Answer: Mustard plant seeds are small, oval-shaped, and possess a seed coat with embryonic structures like cotyledons and embryonic axis. -
How does the external morphology of a mustard plant stem differ from its root?
Answer: The stem is usually above ground, green, and bears leaves and reproductive structures, while the root is below ground, usually brown, and mainly serves for anchorage and absorption of water and nutrients. -
Explain the importance of studying the external morphology of plants.
Answer: Studying external morphology helps in plant identification, understanding plant adaptations, and predicting ecological roles. -
Why is microscopic examination important in plant biology?
Answer: Microscopic examination reveals the internal structure of plant tissues, providing insights into their functions and adaptations. -
How does the arrangement of vascular bundles in a mustard plant stem aid in its function?
Answer: The arrangement provides mechanical strength and facilitates the transport of water, minerals, and nutrients throughout the plant. -
Discuss the role of stomata in mustard plant leaves.
Answer: Stomata regulate gas exchange, allowing for the uptake of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and the release of oxygen and excess water vapor. -
What adaptations do mustard plant flowers exhibit for pollination?
Answer: Mustard plant flowers have bright yellow petals and produce nectar to attract pollinators like bees and butterflies. -
Describe the structure of a mustard plant fruit.
Answer: Mustard plant fruit, known as a silique, is elongated and cylindrical, containing multiple seeds arranged in a linear fashion. -
How do mustard plant seeds disperse?
Answer: Mustard plant seeds are dispersed through various means, including wind, water, and attachment to animals or human activities. -
What ecological role do mustard plants play?
Answer: Mustard plants serve as food sources for herbivores, contribute to soil stabilization, and may exhibit allelopathic effects on other plants. -
Explain the significance of studying the microscopic structure of plant roots.
Answer: Understanding root structure helps in understanding nutrient uptake, root-shoot interactions, and plant responses to environmental stresses. -
How do you differentiate between monocot and dicot seeds?
Answer: Monocot seeds have one cotyledon, while dicot seeds have two cotyledons.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
-
What is the scientific name of the mustard plant?
- Brassica rapa
- Brassica oleracea
- Brassica nigra
- Brassica juncea
Answer: d. Brassica juncea
-
Which part of the mustard plant is typically used for microscopic examination?
- Root
- Stem
- Leaf
- Flower
Answer: a. Root
-
What type of tissue is primarily found in the stem of a mustard plant?
- Epidermal tissue
- Vascular tissue
- Cork tissue
- Mesophyll tissue
Answer: b. Vascular tissue
-
Which of the following is NOT a part of the flower in a mustard plant?
- Stigma
- Style
- Anther
- Calyx
Answer: d. Calyx
-
What is the primary purpose of examining the seeds of a mustard plant microscopically?
- To identify the reproductive structures
- To determine the genetic makeup
- To assess the seed viability
- To study the seed dispersal mechanisms
Answer: c. To assess the seed viability
🔗 Other Useful Links
- News By Amurchem
- Free Web Development Course
- All-in-One Exam Prep Portal
- Articles by Amurchem
- Grade 12 Section
- Grade 11 Section
- Grade 10 Section
- Grade 09 Section
- Advanced Artificial Course
- Home and Online Tuition
- Labs By Amurchem
- Science Lectures By Amurchem
- Social Media Executive Course
© 2025 AmurChem. All rights reserved.






